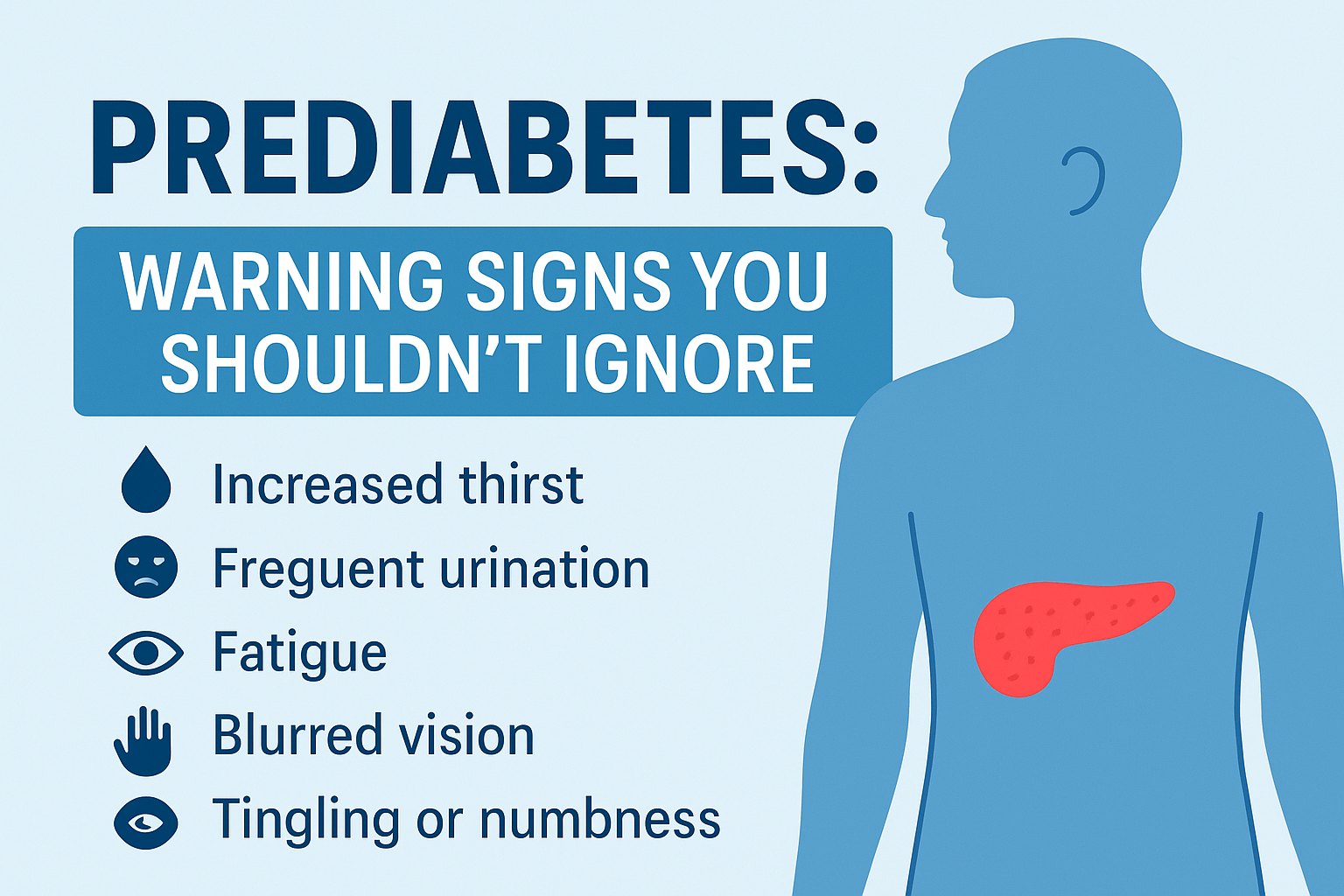
Symptoms of Diabetes:
Early signs of diabetes occur when there’s too much sugar in the blood. Type 1 diabetes shows up with severe symptoms that happen quickly, often in just a few days or weeks. But with type 2 diabetes, signs might not show up until other long-term health problems show up.
Some symptoms are the same for both types of diabetes, but they might be easy to ignore. It’s worrying that many people who have diabetes don’t know they have it. This delay can make it harder to take care of and raise the chance of having more health problems later on.
Numbness
Frequent Thirst
Extreme Hunger
Unexplained Weight Loss
Fatigue
Blurry vision
Chronic Infections
Dark Patches of Skin
Numbness:
Numbness, particularly in the hands or feet, can be a symptom of diabetic neuropathy, a type of nerve damage caused by prolonged high blood sugar levels. Over time, elevated blood glucose levels can lead to nerve damage, resulting in tingling, numbness, or loss of sensation in affected areas.
Frequent Thirst:
Frequent thirst, known as polydipsia, is a common symptom of diabetes. High blood sugar levels lead to increased urine production, causing dehydration and triggering the sensation of thirst. Excessive thirst is often one of the early signs of diabetes and may indicate poor blood sugar control.
Extreme Hunger:
Extreme hunger, or polyphagia, is another common symptom of diabetes. Insulin resistance or insufficient insulin production prevents glucose from entering cells for energy, leading to increased hunger despite adequate food intake. This constant feeling of hunger is a result of the body’s inability to use glucose effectively for energy.
Unexplained Weight Loss:
Unexplained weight loss can occur in individuals with undiagnosed or poorly managed diabetes. When cells are unable to receive glucose for energy due to insulin resistance or deficiency, the body starts breaking down fat and muscle tissue for fuel, resulting in unintentional weight loss despite normal or increased food intake.
Fatigue:
Fatigue is a common symptom of diabetes, often attributed to fluctuations in blood sugar levels. High blood sugar levels can lead to fatigue due to cells being unable to access glucose for energy production. Additionally, diabetes-related complications such as neuropathy, kidney disease, or poor sleep quality may contribute to fatigue.
Blurry Vision:
Blurry vision can be an early sign of diabetes, particularly when blood sugar levels are consistently high. Elevated blood glucose levels can cause swelling of the lenses in the eyes, leading to changes in vision. Blurry vision may also result from damage to blood vessels in the retina (diabetic retinopathy), a common complication of diabetes.
Chronic Infections:
Chronic infections, such as urinary tract infections, skin infections, or yeast infections, can be more common and recurrent in individuals with diabetes. High blood sugar levels create a favorable environment for bacterial and fungal growth, impairing the body’s ability to fight off infections. Poor circulation and compromised immune function due to diabetes can also contribute to chronic infections.
Dark Patches of Skin:
Dark patches of skin, known as acanthosis nigricans, can occur in individuals with insulin resistance or type 2 diabetes. This condition is characterized by thickened, velvety, darkened skin, commonly found in skin folds such as the neck, armpits, or groin. Acanthosis nigricans is often associated with insulin resistance and obesity, though it can also occur in individuals with type 1 diabetes.